The physical part of an electronic circuit is the circuit board. Electrical current conductivity is its primary function. Circuit boards are available in a variety of sizes and shapes. Surface-mount, Through-hole, and Flex PCBs are the three categories. Listed below are the differences between these types of circuit boards and what they are used for.
Four-Layer PCBs
A four-layer PCB is a type of PCB that has four conductive layers. The top layer is generally used as a power plane, and the two inner layers act as ground planes. The bottom layer is used to place components. The outer layers typically have exposed pads that provide placement locations for surface-mount devices. The layers are connected via holes. The four layers are then laminated together to form one board.
Four-layer PCBs are more expensive than their two-layer cousins. However, they do provide higher-quality performance and more flexibility in design. A four-layer PCB allows more components to be placed on a single board and offers improved durability.
High-speed signals usually require a relative path for return current. This makes it easier to route the call on the outer layers. However, power planes and ground planes must be separated to avoid interference. Putting the signal on the ground plane can minimize the voltage drop on the power rail. As the heart of all electronics, printed circuit boards are naturally most susceptible to damage, which would result in an immediate power outage. There are circuit board repair supplies key largo fl that people could take advantage of when in need.
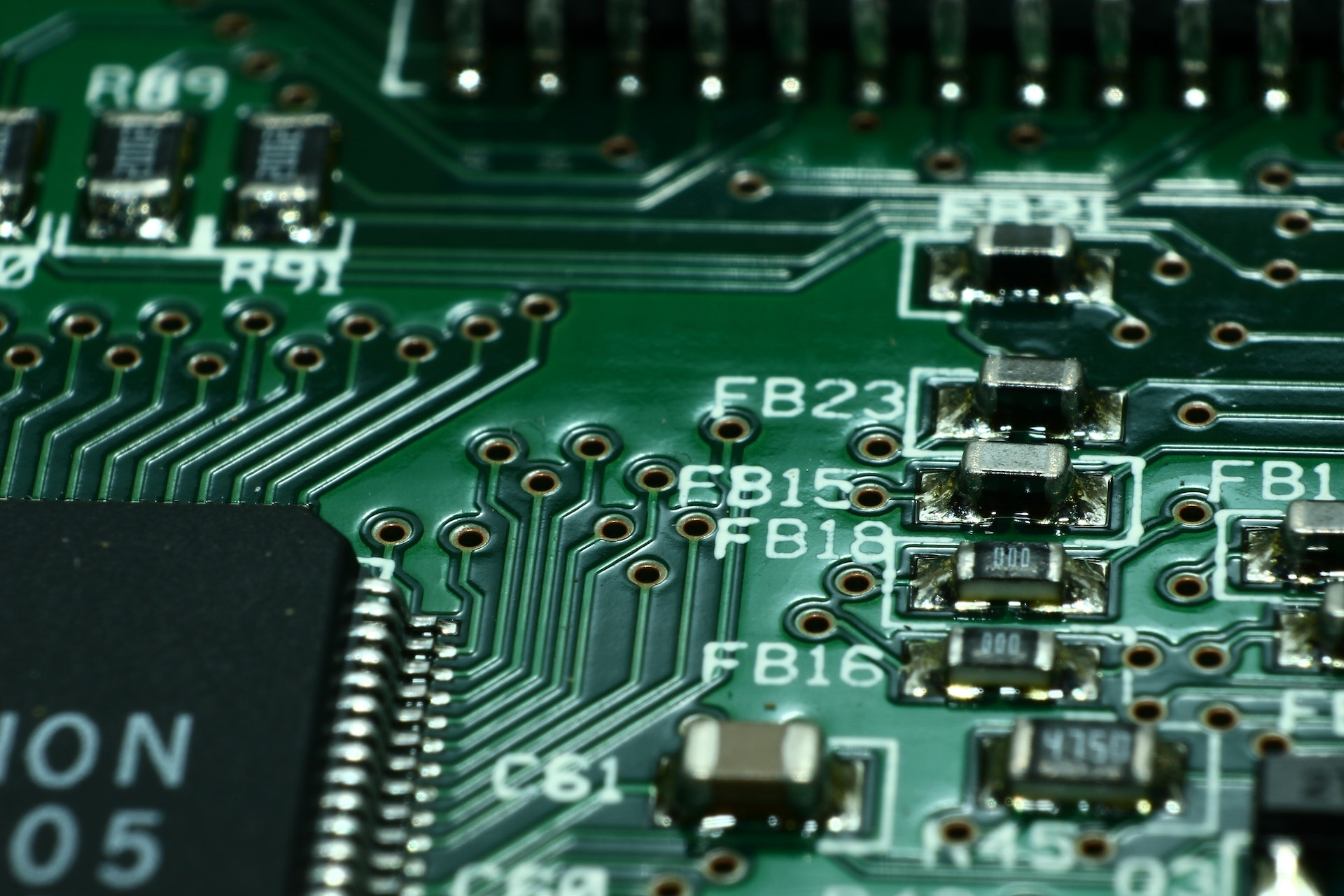
Surface-Mount PCBs
Surface-mount PCBs are a common component found in nearly all electronic devices today. These boards are made up of tiny details attached to each other with solder. This type of technology is primarily used for automation. It provides greater flexibility and capability than other forms of PCBs.
This technology is ideal for quick PCB production and is far cheaper than manual construction methods. Although they are more expensive to manufacture, manual assembly does have its uses, such as for prototyping. This is a process where a PCB design is refined until it’s ready to be mass-produced.
Surface-mount PCBs are smaller than conventional PCBs and often have lower power ratings than their counterparts with lead-in packages. They can also be more compact, with power dissipation of fewer than 0.25 watts.
Through-Hole PCBs
Through-hole PCBs are manufactured by printed circuit board assembly services and are commonly used in military and aerospace equipment that are subject to high temperatures, forceful collisions, and rapid accelerations. Because of these characteristics, through-hole PCBs are an excellent choice for such rugged products. These boards also allow engineers to avoid the risks of stray inductance from wire leads.
Through-hole PCBs are commonly used in military and aerospace equipment, subject to high temperatures, forceful collisions, and rapid accelerations. Because of these characteristics, through-hole PCBs are an excellent choice for such rugged products. These boards also allow engineers to avoid the risks of stray inductance from wire leads.
Through-hole technology guarantees higher density, better component selection, and stronger bonds between layers. This technology is also popular in high-reliability products. These boards are typically thicker and more extensive than their SMT counterparts. A further benefit is that they can withstand more significant environmental stress than SMT components.




Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.